Module 4
Foundations for Fraction Operations
- 6 TOPICS
- 34 LESSONS
In module 4, students rename fractions greater than 1 as mixed numbers, generate equivalent fractions, compare fractions with unlike units, and add and subtract fractions and mixed numbers with like units. Students also multiply fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers.
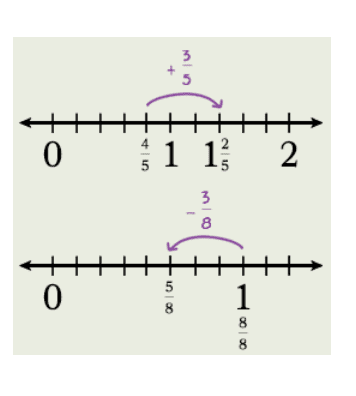
Topic E
Add and Subtract Mixed Numbers
8 LESSONS
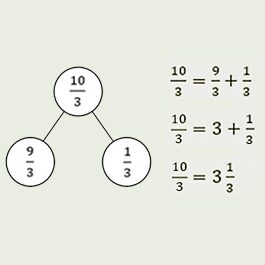
Students add a fraction to a mixed number and add two mixed numbers. They also subtract a fraction from a mixed number and subtract two mixed numbers. Students apply previously learned strategies for adding and subtracting whole numbers to add and subtract mixed numbers. They use number bonds, the arrow way, and an open number line to represent and record the addition and subtraction. Understanding a mixed number as a sum of a whole number and a fraction helps students as they compose and decompose mixed numbers to add and subtract. Students create and interpret line plots, including solving addition and subtraction problems with fractional data.
- 4.MD.A.2Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, liquid volumes, masses of objects, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals, and problems that require expressing measurements given in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Represent measurement quantities using diagrams such as number line diagrams that feature a measurement scale.
- 4.MD.B.4Make a line plot to display a data set of measurements in fractions of a unit (1/2, 1/4, 1/8). Solve problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions by using information presented in line plots.For example, from a line plot find and interpret the difference in length between the longest and shortest specimens in an insect collection.
- 4.NF.B.3.cAdd and subtract mixed numbers with like denominators, e.g., by replacing each mixed number with an equivalent fraction, and/or by using properties of operations and the relationship between addition and subtraction.
- 4.NF.B.3.dSolve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole and having like denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem.
Topic D
Add and Subtract Fractions
5 LESSONS
Students estimate to assess reasonableness when solving word problems to establish an underlying theme for the topic. They add and subtract fractions with like units and subtract a fraction from a whole number. Using unit form and a number line helps students relate their previous work with adding and subtracting whole numbers to adding and subtracting fractions. They see similar part-total relationships and the importance of adding and subtracting like units. Students may apply their part-total understanding to think of a subtraction problem as an unknown addend problem. In an optional lesson, students add fractions with related units by generating equivalent fractions.
- 4.MD.A.2Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, liquid volumes, masses of objects, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals, and problems that require expressing measurements given in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Represent measurement quantities using diagrams such as number line diagrams that feature a measurement scale.
- 4.NF.B.3.aUnderstand addition and subtraction of fractions as joining and separating parts referring to the same whole.
- 4.NF.B.3.bDecompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way, recording each decomposition by an equation. Justify decompositions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.Examples: 3/8 = 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8; 3/8 = 1/8 + 2/8; 2 1/8 = 1 + 1 + 1/8 = 8/8 + 8/8 + 1/8.
- 4.NF.B.3.dSolve word problems involving addition and subtraction of fractions referring to the same whole and having like denominators, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem.
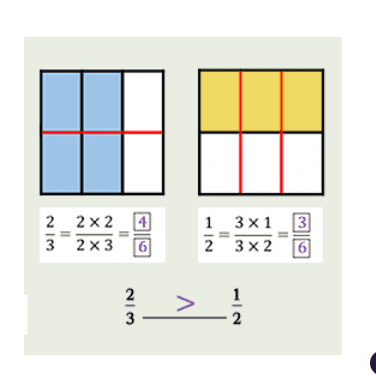
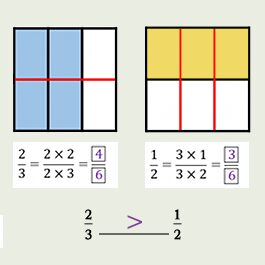
Topic C
Compare Fractions
5 LESSONS
Students use various methods to compare fractions less than 1, fractions greater than 1, and mixed numbers. They consider the relationship between the numbers and use what they know about unit fractions to compare fractions to benchmark numbers such as 0, 12 , and 1. When the fractions have related numerators or denominators, students use what they know about generating equivalent fractions to rename one fraction to create a common numerator or common denominator. They rename both fractions as equivalent fractions to compare any two fractions. They use similar methods to compare fractions greater than 1 and mixed numbers.
4.NF.A.2 Compare two fractions with different numerators and different denominators, e.g., by creating common denominators or numerators, or by comparing to a benchmark fraction such as 1/2. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
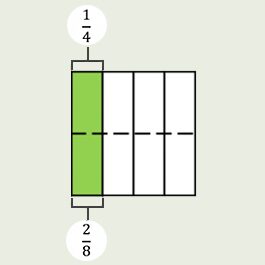
Topic B
Equivalent Fractions
6 LESSONS
Students generate equivalent fractions and equivalent mixed numbers. They decompose fractional units to find an equivalent fraction with smaller units and record their work with multiplication. They compose fractional units to find an equivalent fraction with larger units and record their work with division. Students use area models, as well as tape diagrams and number lines, to represent fractions and compose or decompose fractional units to generate equivalent fractions.
- 4.NF.A.1 Explain why a fraction 𝑎/𝑏 is equivalent to a fraction (𝑛 × 𝑎)/(𝑛 × 𝑏) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions.
- 4.NF.B.3.a Understand addition and subtraction of fractions as joining and separating parts referring to the same whole.
- 4.NF.B.3.b Decompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way, recording each decomposition by an equation. Justify decompositions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.Examples: 3/8 = 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8; 3/8 = 1/8 + 2/8; 2 1/8 = 1 + 1 + 1/8 = 8/8 + 8/8 + 1/8.
Topic A
Fraction Decomposition and Equivalence
6 LESSONS
Students decompose fractions into a sum of unit fractions and into a sum of non-unit fractions. They use familiar models such as number bonds, tape diagrams, and number lines to represent fractions. They recognize that the area model may be a useful model to represent fractions. Students decompose fractions greater than 1 into a sum of a whole number and a fraction less than 1. This decomposition helps students rename fractions greater than 1 as equivalent mixed numbers. Students express mixed numbers as a sum of a whole number and a fraction less than 1. Then they rename the whole number as an equivalent fraction that they then add to the fraction. This helps students rename mixed numbers as equivalent fractions greater than 1.
- 4.NF.B.3.aUnderstand addition and subtraction of fractions as joining and separating parts referring to the same whole.
- 4.NF.B.3.bDecompose a fraction into a sum of fractions with the same denominator in more than one way, recording each decomposition by an equation. Justify decompositions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.Examples: 3/8 = 1/8 + 1/8 + 1/8; 3/8 = 1/8 + 2/8; 2 1/8 = 1 + 1 + 1/8 = 8/8 + 8/8 + 1/8.
Multiplication and Division of Multi-Digit Numbers
In module 3, students multiply numbers of up to four digits by one-digit numbers and two-digit numbers by two-digit numbers. Students also divide numbers of up to four digits by one-digit numbers, resulting in whole-number quotients and remainders.
- 6 TOPICS
- 24 LESSONS
Module 3
Topic D
Multiplication of Two-Digit Numbers by Two-Digit Numbers
5 LESSONS
Standard: 4.NBT.B.5
Students apply the associative and distributive properties to multiply a two-digit number by a multiple of 10 and then progress to multiplying two-digit numbers by two-digit numbers. Area models are used to represent the multiplication and to help students recognize how each factor is broken apart and multiplied. Students see that each part of one factor is multiplied by each part of the other factor. They record four partial products in the area model and in vertical form alongside the area model and then transition to recording two partial products in the same way. Students add the partial products to find the product.
Topic C
Multiplication of up to Four-Digit Numbers by One-Digit Numbers
4 LESSONS
Standard: 4.NBT.B.5
Students apply the distributive property to multiply numbers of up to four digits by one-digit numbers. They break apart the larger factor by place value and multiply the number of each unit by the one-digit factor. They represent the multiplication by using place value charts, area models, and vertical form. Students record partial products in vertical form by recording each partial product separately and by recording them together on one line.
- Topic B: Division of Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, and Ones
- 5 lessons
- Standards
- 4.NBT.B.6
Students divide numbers of up to four digits by one-digit numbers. They draw an area model, represent the divisor as one side length, and compose the unknown side length by building up to the total. Students also represent the division on a place value chart. They decompose the totals into place value units, divide each unit, and record long division in vertical form alongside the place value chart to reinforce conceptual understanding. They recognize that, although the value of the unit is different, the process of dividing each unit remains the same.
Topic A
Multiplication and Division of Multiples of Tens, Hundreds, and Thousands
Students multiply and divide multiples of 10, 100, and 1000 by focusing on place value units. They use place value disks and write equations in unit form to help them recognize that they can use familiar multiplication and division facts to find products and quotients. Application of the associative property helps students to rewrite two-factor multiplication expressions as three-factor expressions so, again, they can multiply by using familiar facts. To help prepare for multiplication of two-digit numbers by two-digit numbers, an area model is used to show that multiplying a multiple of 10 by a multiple of 10 results in a number with the unit of hundreds.
3 LESSONS
- 4.NBT.B.5
- 4.NBT.B.6
Module 6 Topic A
Topic A
Lines and Angles
Students define, name, and draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles, parallel lines, perpendicular lines, and intersecting lines. They identify different types of angles and describe them in relationship to each other (e.g., an obtuse angle is larger than a right angle and smaller than a straight angle). Students use their understanding of the words parallel, perpendicular, and intersecting to identify and name relationships between lines, line segments, rays, and sides in polygons.


Students define, name, and draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles, parallel lines, perpendicular lines, and intersecting lines. They identify different types of angles and describe them in relationship to each other (e.g., an obtuse angle is larger than a right angle and smaller than a straight angle). Students use their understanding of the words parallel, perpendicular, and intersecting to identify and name relationships between lines, line segments, rays, and sides in polygons.
Module 2 Place Value Concepts for Multiplication and Division
In module 2, students multiply two-digit numbers by one-digit numbers by using the distributive property. They divide two- and three-digit numbers by one-digit numbers by using the break apart and distribute strategy. Students apply their multiplication skills to convert customary units of length. They also identify factors and multiples of numbers within 100.
- 5 TOPICS
- 26 LESSONS
Topic A Standards (Lessons 1-3)
- 4.NBT.B.5Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
- 4.NBT.B.6Find whole-number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
- 4.MD.A.3Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems.For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor.
Topic B (Lessons 4-10)
- 4.OA.A.2Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative comparison, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem, distinguishing multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.
- 4.NBT.B.5Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
- 4.MD.A.3Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems.For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor.
- Topic C: Division of Tens and Ones by One-Digit Numbers (lessons 11-16)
- 4.NBT.B.6Find whole-number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Multiplication of Tens and Ones by One-Digit Numbers
Module 1: Place Value Concepts for Addition and Subtraction
- 5 TOPICS
- 24 Assignments
In module 1, students use multiplicative comparisons to describe place value relationships and the relative sizes of metric units. They build fluency with the standard algorithm for addition and subtraction with numbers of up to 6 digits.
Topic A Standards (Lessons 1-4):
- 4.OA.A.1Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 × 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations.
- 4.OA.A.2Multiply or divide to solve word problems involving multiplicative comparison, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem, distinguishing multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.
Topic B Standards (Lessons 5-9):
- 4.OA.A.1Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison, e.g., interpret 35 = 5 × 7 as a statement that 35 is 5 times as many as 7 and 7 times as many as 5. Represent verbal statements of multiplicative comparisons as multiplication equations.
- 4.NBT.A.1Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right.For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division.
- 4.NBT.A.2Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
Topic C Standards (Lessons 10-15):
- 4.OA.A.3Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
- 4.NBT.A.2Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form. Compare two multi-digit numbers based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons.
- 4.NBT.A.3Use place value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place.
Topic D Standards (Lessons 16-22):
- 4.OA.A.3Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.
- 4.NBT.B.4Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
Topic E Standards (Lessons 23-24):
- 4.MD.A.1Know relative sizes of measurement units within one system of units including km, m, cm; kg, g; lb, oz.; l, ml; hr, min, sec. Within a single system of measurement, express measurements in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Record measurement equivalents in a two-column table.For example, know that 1 ft is 12 times as long as 1 in. Express the length of a 4 ft snake as 48 in. Generate a conversion table for feet and inches listing the number pairs (1, 12), (2, 24), (3, 36),…
- 4.MD.A.2Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, liquid volumes, masses of objects, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals, and problems that require expressing measurements given in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Represent measurement quantities using diagrams such as number line diagrams that feature a measurement scale.